Difference between revisions of "ButtonBoxes"
| Line 404: | Line 404: | ||
===Presentation=== | ===Presentation=== | ||
| − | See chapter 8 in the presentation | + | See chapter 8 in the presentation manual by clicking [http://tsgdoc.socsci.ru.nl/images/9/9e/Programming_with_Presentation_2013.pdf here] |
Revision as of 08:52, 7 August 2015
| 300px 2013 Buttonbox | |
| Downloads | |
|---|---|
The buttonbox is used for time accurate(1ms) button press registration. We use it to register buttonpresses, soundkey, voicekey signals and to send tone onset, analog output, triggers with the BITSI protocol. It is suitable for Behavioral, EEG, MEG, and fMRI experiments. The buttonbox is connected to a computer with a usb connection.
The output connector has two binary eight bit ports: input and output. The two ports can be used for responses (input) and stimulus triggers (output). Two 8 bits analog outputs and three 8 bits analog inputs. The output connector has a sound and voicekey which triggers when a amplitude reaches a threshold. By using the serial port, the BITSI can be used platform independently: it works on Windows, Linux and Mac OSX. Most programming environments and stimulus packages support serial communication.
BITSI Protocol
BITSI stands for Bits to Serial Interface. Because the BITSI is designed to interface both in- and output signals, the 'protocol' is asymmetric: the input and output protocols differ.
Input
The input port can be used to interface eight buttons maximally. Button presses are translated to serial output characters/bytes according to the following table:
| BITSI Simple | ||
|---|---|---|
| Signal/Button | ASCII (rise/fall) | Code (rise/fall) |
| 1 | A / a | 65 / 97 |
| 2 | B / b | 66 / 98 |
| 3 | C / c | 67 / 99 |
| 4 | D / d | 68 / 100 |
| 5 | E / e | 69 / 101 |
| 6 | F / f | 70 / 102 |
| 7 | G / g | 71 / 103 |
| 8 | H / h | 72 / 104 |
| Soundkey | S / s | 83 / 115 |
| Voicekey | V / v | 86 / 118 |
This means that when signal 1 gets active(button press), a capital A will be sent to the serial port. A lowercase 'a' will be sent when the signal is deactivated(button release). Mechanical buttons can be connected directly.
Output
Output knows two protocols: BITSI simple or BITSI extended. To enter a certain protocol two buttons have to be pressed when the BITSIbox is powered. Press button H and A for simple mode and H and B for extended mode.
If no button is pressed when powered it boots the last known protocol. In the simple protocol every byte sent to the BITSI over the serial port, is represented at the 8 bit output.
The extended protocol uses two bytes(or two characters), this combination can access two analog outputs and a tone generator. The first byte selects the output. The second byte determines the value written to this output.
| BITSI Extended | ||
|---|---|---|
| Function | Byte 1 (ASCII/code) | Byte 2 |
| Marker Out | M / 77 | Marker Value |
| Pulse Out | P / 80 | Marker Value |
| Pulse Time | X / 88 | ms before pulse reset |
| Analog Out 1 | Y / 89 | Analog Output Value |
| Analog Out 2 | Z / 90 | Analog Output Value |
| Tone | T / 84 | Start Tone |
| Detect Sound | D / | S / 83 |
| Detect Voice | D / | V / 83 |
| Calibrate Sound | C / | S |
| Calibrate Voice | C / | V |
| Analog In 1 | A / | 1 |
| Analog In 2 | A / | 2 |
| Analog In 3 | A / | 3 |
| Analog In 4 | A / | 4 |
| LEDs Off | L / | X |
| LEDs Input | L / | I |
| LEDs Output | L / | O |
Port Settings
Trigger port
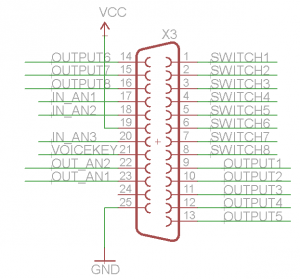
The 25 pins female connector has 8 inputs and 8 outputs, respectively 1-8 are inputs and 9-16 are outputs. Three analog input with an analog to digital convertor of 12 bit, pins 17,18,20 and 21. Two analog outputs with an digital to analog convertor of 12 bits on pins 22 and 23.
Serial port
Our hardware design allows to be connected to the computers USB and emulates a serial communication Port.
| Baudrate | 115200 |
| Parity | None |
| Data bits | 8 |
| Stop bits | 1 |
| Flow control | None |
USB-Com port
1.Connect the BITSIbox to your computer using the USB cable.
2.When you connect the BITSIbox, Windows should initiate the driver installation process (if you haven't used the computer with an BITSIbox board before).
3.On Windows Vista/7, the driver should be automatically downloaded and installed.
4.On Windows XP, the Add New Hardware wizard will open:
- When asked Can Windows connect to Windows Update to search for software? select No, not this time. Click next.
- Select Install from a list or specified location (Advanced) and click next.
- Make sure that Search for the best driver in these locations is checked; uncheck Search removable media; check Include this location in the search and browse to the c:/beheer/arduino/drivers directory.
- The wizard will search for the driver and then tell you that a "USB Serial Converter" was found. Click finish.
- The new hardware wizard will appear again. Go through the same steps and select the same options and location to search. This time, a "USB Serial Port" will be found.
How to Check the Com Port settings(important!)
- From the Start menu, open the Control Panel.
- From the control panel, open the System window.
- From the system properties window, go to the Hardware tab and click the Device Manager button.
- From the Device Manager window, click Ports (Com&LPT). You should now be able to see which Com Port the USB adapter is assigned to.
- If the Com Port is 10 or higher, you will have to change it to a lower port.
- From the Device Manager window, click on USB Serial Port (Com#). Click the Port Settings tab of the USB Serial Port Properties window, and then click the Advanced button.
- In the Advanced Settings window, use the scroll input to select a Com Port (select 10 or lower). Change Receive (bytes) and Transmit (bytes) to 64. Change the Latency Timer to 1.
- Click the OK button.
Always connect the usb device to the same port and your settings will be remembered.
Software Settings
Neurobs Presentation
The experiment files needs a few settings for the device to work:
- In the settings tab: port -> input port -> 1 must be the device that identifies itself as "Arduino Uno" in the device manager. Note that the port must have a number not higher than 10 (COM1-COM10). Use re-enumerate if it is higher.
- Rate must be set 115200, Parity to None, Data Bits to 8 and Stop Bits to 1, Uncheck FIFO Interrupt.
Python/PsychoPy
Download this site package to use the buttonbox: rusocsci
Example using buttons from the buttonbox in Python:
1#!/usr/bin/env python
2
3# import the rusocsci.buttonbox module
4from rusocsci import buttonbox
5
6# make a buttonbox
7bb = buttonbox.Buttonbox()
8
9# wait for a single button press
10b = bb.waitButtons()
11
12# print the button pressed
13print("b: {}".format(b))
Example using markers with the buttonbox in Python:
1#!/usr/bin/env python
2
3# import the rusocsci.buttonbox module
4from rusocsci import buttonbox
5
6# make a buttonbox
7bb = buttonbox.Buttonbox()
8
9# wait for a single button press
10bb.sendMarker(val=100) #This is your marker code, range code 1-255
Example using the Buttonbox in PsychoPy:
1#!/usr/bin/env python
2
3# import psychopy and rusocsci
4from psychopy import core, visual
5from rusocsci import buttonbox
6
7## Setup Section
8win = visual.Window(monitor="testMonitor")
9bb = buttonbox.Buttonbox()
10text = visual.TextStim(win, "Press a button on the buttonbox")
11
12## Experiment Section
13# show text
14text.draw()
15win.flip()
16# wait for response
17b = bb.waitButtons()
18# show response
19text.setText("you pressed: {}".format(b))
20text.draw()
21win.flip()
22core.wait(5)
23
24## Cleanup Section
25core.quit()
For more documentation click here: http://pythonhosted.org//RuSocSci/index.html
Matlab
1function handle = buttonbox(cmd,varargin)
2% to initialize connection:
3% define settings as structure with fields:
4% bb.Device = 'COM2';
5% bb.BaudRate = 115200;
6% bb.DataBits = 8;
7% bb.StopBits = 1;
8% bb.Parity = 'none';
9% handle = buttonbox('open',bb)
10%
11% to run:
12% buttonbox('run',handle);
13%
14% to close the connection:
15% buttonbox('close',handle);
16
17persistent old_hdl % keep handle to COM object persistent
18
19% set defaults
20bb.Device = 'COM2';
21bb.BaudRate = 115200;
22bb.DataBits = 8;
23bb.StopBits = 1;
24bb.Parity = 'none';
25
26if nargin < 1
27 cmd = 'open';
28end
29if nargin > 1
30 % user overwrites default settings
31 flds = fields(varargin{1});
32 for n = 1 : numel(flds)
33 bb.(flds{n}) = varargin{1}.(flds{n});
34 end
35end
36
37
38switch cmd
39 case 'open'
40 % get handle to serial device
41 handle = open_buttonbox(bb);
42 return
43 case 'close'
44 if nargin > 0
45 handle = varargin{1};
46 else
47 handle = old_hdl;
48 end
49 fclose(handle);
50 return
51 case 'run'
52 % read incoming data
53 if isempty(old_hdl)
54 help serial_buttonbox_common
55 error('Buttonbox not yet initialized');
56 end
57 handle = old_hdl;
58 otherwise
59 fprintf('Unknown option %s\n',cmd);
60 return
61end
62
63% only gets here when cmd = 'run'
64% Initialize output figure
65win = list_output(' ',[]);
66while 1
67 % Exit if user closed output figure
68 if ~ishandle(win)
69 return
70 end
71 % start polling for characters (indicating start of scan)
72 navailable = handle.BytesAvailable;
73 if navailable
74 data = [];
75 while navailable
76 % read incoming data
77 [newdata, cnt] = fread(handle, navailable);
78 % concatenate possible new data
79 if cnt
80 data = [data newdata(:)];
81 end
82 % check if any more data left
83 navailable = handle.BytesAvailable;
84 end
85 % output info about which button was pressed
86 for n = 1 : numel(data)
87 line = sprintf('incoming: %03d %s',data(n),char(data(n)));
88 list_output(line,win);
89 end
90 end
91 pause(0.01);
92end %while 1
93
94 function hdl = open_buttonbox(device)
95 % open handle to serial device (mini buttonbox)
96 try
97 hdl = serial(device.Device, 'Baudrate', device.BaudRate, 'DataBits', device.DataBits, 'StopBits', device.StopBits, 'Parity', device.Parity);
98 fopen(hdl);
99 catch
100 if ~isempty(old_hdl)
101 fclose(old_hdl);
102 delete(old_hdl);
103 end
104 hdl = serial(device.Device, 'Baudrate', device.BaudRate, 'DataBits', device.DataBits, 'StopBits', device.StopBits, 'Parity', device.Parity);
105 fopen(hdl);
106 end
107 old_hdl = hdl;
108
109 fprintf('Wait for device buttonbox....\n');
110 tic
111 while hdl.BytesAvailable && toc<10
112 navailable = bbox.BytesAvailable;
113 % wait for welcome message device
114 fread(hdl, navailable);
115 end
116 pause(0.5);
117 end
118
119 function win = list_output(line,win)
120 persistent ptr
121 persistent lines
122 persistent edt
123 Maxlines = 40;
124
125 if isempty(win)
126 % initialize listbox output figure
127 lines = cell(1,Maxlines);
128 [lines(1:end)]=deal({''});
129 ptr=Maxlines;
130 lines(ptr) = {'Buttonbox output:'};
131 idxs = mod(ptr:ptr+Maxlines-1,Maxlines)+1;
132
133 win = figure();
134 % initialize figure to hold output text
135 edt = uicontrol('Parent',win,'Style','ListBox','HorizontalAlignment','left', ...
136 'Max',Maxlines,'BackgroundColor',[1 1 1],'Visible','on','String',lines(idxs), ...
137 'FontSize',12,'Value',Maxlines);
138 pos = get(win,'Position');
139 set(edt,'Position',[1 1 pos(3) pos(4)]);
140 end
141 ptr = mod(ptr,Maxlines)+1; % start
142 lines{ptr} = line;
143 idxs = mod(ptr:ptr+Maxlines-1,Maxlines)+1;
144 set(edt,'String',lines(idxs),'Value',Maxlines);
145 drawnow;
146 end
147
148end
Markers
Presentation
See chapter 8 in the presentation manual by clicking here