Difference between revisions of "Audio delay"
(Created page with "Audio delay is the time between the moment the experimenter want the audio to be played and the start of the audio playing. For experiments where no distinction is made betwe...") |
|||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
# the time difference between the onsets on the trigger and the audio signal is measured on the oscilloscope | # the time difference between the onsets on the trigger and the audio signal is measured on the oscilloscope | ||
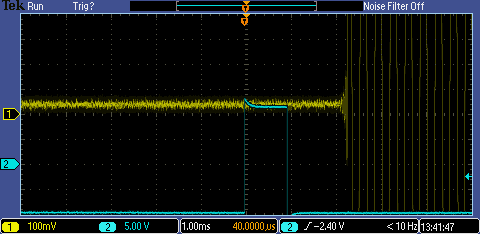
| − | This | + | This is an example of audio delay measured with the oscilloscope test. |
| − | [[File:Alsa.png| | + | |
| + | [[File:Alsa.png|border|Example audio delay of about 2ms using the osciloscope test.]] | ||
=== Precision test === | === Precision test === | ||
This test does not measure the audio delay itself, but only the precision. It can be combined with the previous test | This test does not measure the audio delay itself, but only the precision. It can be combined with the previous test | ||
Revision as of 09:29, 17 December 2018
Audio delay is the time between the moment the experimenter want the audio to be played and the start of the audio playing. For experiments where no distinction is made between systematic and random errors in timing, the audio delay equals the accuracy of the onset of the audio stimulus.
Neurobs presentation
These are measurements of the audio delay in Neurobs Presentation on the Faculty of Social Sciences (DCC and BSI) labcomputer with three different settings. Note that exclusive mode is most used in experiments and is the mode best comparable with for instance Linux Alsa. Shared mode is best comparable with Linux Jack.
Presentation, Exclusive Mode
Presentation, DirectX Mode
Alternative definitions
Round trip test
This is the definition used above.
- the audio stimulus is prepared
- a random delay is applied
- the virtual stopwatch is started
- the audio stimulus is started immediately after the stopwatch
- the line output of the audio hardware is connected to the sound or voice detector of the buttonbox
- the buttonbox reports receiving the audio, the virtual stopwatch is stopped
This loop is repeated a number of times to get a good estimate of the statistical distribution of the delay.
Oscilloscope test
This test more accurately measures the delay, since no loop back to the computer is needed. The test is more work to perform and therefore less useful for determining the statistical distribution of the delay.
- the audio stimulus is prepared
- a random delay is applied
- a trigger is sent to the buttonbox, the trigger show on one channel of the oscilloscope
- the audio stimulus is started
- the line output of the audio hardware is connected to another channel of the oscilloscope
- the time difference between the onsets on the trigger and the audio signal is measured on the oscilloscope
This is an example of audio delay measured with the oscilloscope test.
Precision test
This test does not measure the audio delay itself, but only the precision. It can be combined with the previous test